- Do you want to share a Python script to a friend that doesn’t have Python installed? In this post you’ll learn how 🙂 With the py2app package you can compile a Python script and create a portable Mac application. If you’re using windows, you can check py2exe. First of all, we need to install the py2app python package.
- How to run a Python script¶. Your best way to get started with Python on Mac OS X is through the IDLE integrated development environment, see section The IDE and use the Help menu when the IDE is running. If you want to run Python scripts from the Terminal window command line or from the Finder you first need an editor to create your script.
- As of Python 3.6, string formatting can be done more elegantly using f-strings, but these require the placeholders to be defined before the f-string itself. In order to define the email message at the beginning of the script, and fill in placeholders for each contact when looping over the CSV file, the older.format method is used.
Run Python scripts. In just a few steps, you can run Python scripts and create a data model. From this model, you can create reports and share them on the Power BI service. Prepare a Python script. First, create a script in your local Python development environment and make sure it runs successfully. For example, here's a simple Python script. Py2app - Create standalone Mac OS X applications with Python¶. Py2app is a Python setuptools command which will allow you to make standalone application bundles and plugins from Python scripts. Py2app is similar in purpose and design to py2exe for Windows. An IP(Internet Protocol) address is an identifier assigned to each computer and other device(e.g., router, mobile, etc) connected to a TCP/IP network that is used to locate and identify the node in communication with other nodes on the network.
Mac OS X comes with Python 2.7 out of the box.
You do not need to install or configure anything else to use Python 2. Theseinstructions document the installation of Python 3.
The version of Python that ships with OS X is great for learning, but it’s notgood for development. The version shipped with OS X may be out of date from theofficial current Python release,which is considered the stable production version.
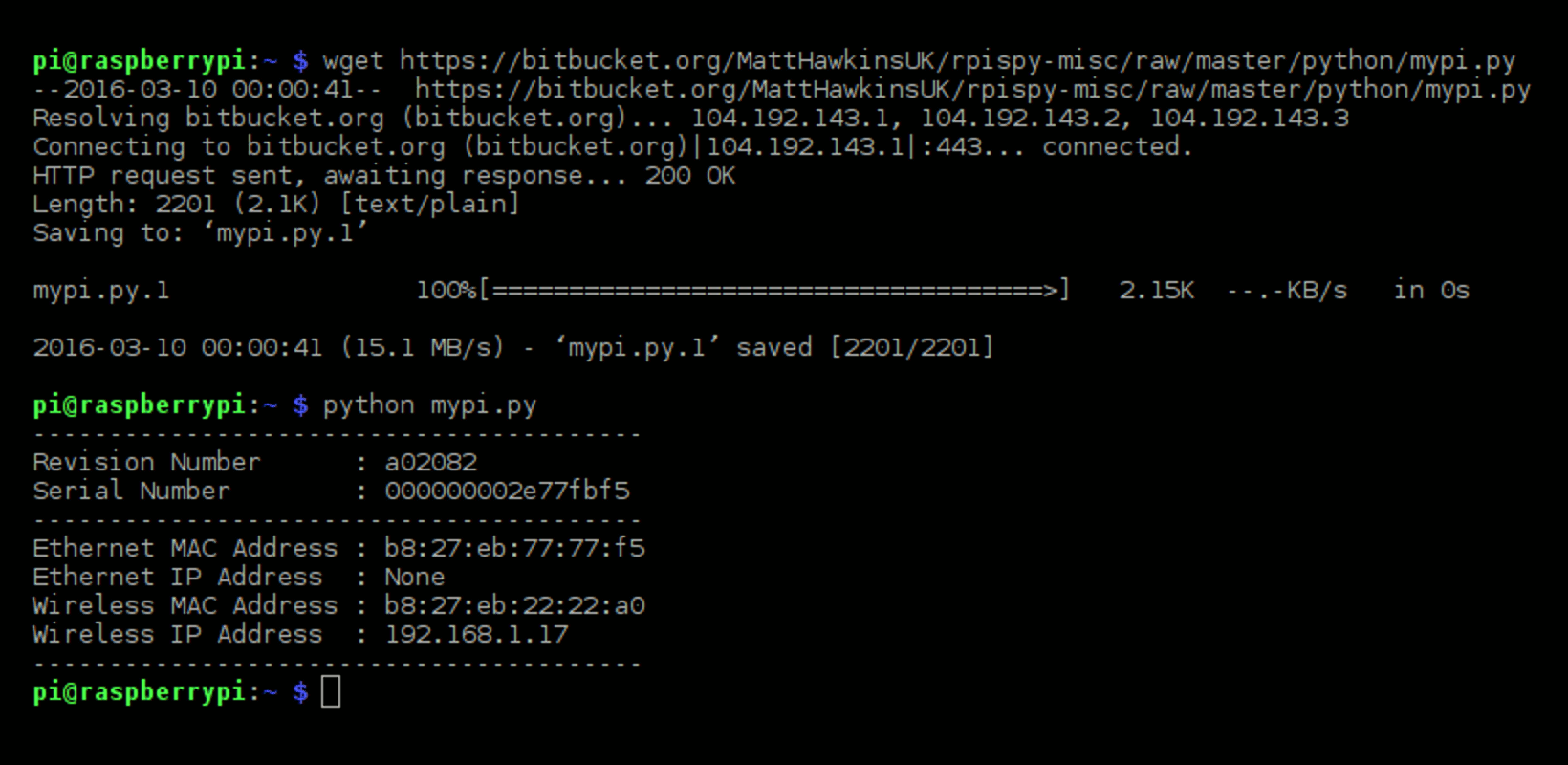
Create Python Executable Mac
Doing it Right¶
Let’s install a real version of Python.
Before installing Python, you’ll need to install GCC. GCC can be obtainedby downloading Xcode, the smallerCommand Line Tools (must have anApple account) or the even smaller OSX-GCC-Installerpackage.
Note
If you already have Xcode installed, do not install OSX-GCC-Installer.In combination, the software can cause issues that are difficult todiagnose.
Note
If you perform a fresh install of Xcode, you will also need to add thecommandline tools by running xcode-select--install on the terminal.

While OS X comes with a large number of Unix utilities, those familiar withLinux systems will notice one key component missing: a package manager.Homebrew fills this void.
To install Homebrew, open Terminal oryour favorite OS X terminal emulator and run
The script will explain what changes it will make and prompt you before theinstallation begins.Once you’ve installed Homebrew, insert the Homebrew directory at the topof your PATH environment variable. You can do this by adding the followingline at the bottom of your ~/.profile file
If you have OS X 10.12 (Sierra) or older use this line instead
Now, we can install Python 3:
This will take a minute or two.
Pip¶
Homebrew installs pip pointing to the Homebrew’d Python 3 for you.
Working with Python 3¶
At this point, you have the system Python 2.7 available, potentially theHomebrew version of Python 2 installed, and the Homebrewversion of Python 3 as well.
Python Script To Mac App
will launch the Homebrew-installed Python 3 interpreter.
will launch the Homebrew-installed Python 2 interpreter (if any).
will launch the Homebrew-installed Python 3 interpreter.
If the Homebrew version of Python 2 is installed then pip2 will point to Python 2.If the Homebrew version of Python 3 is installed then pip will point to Python 3.
The rest of the guide will assume that python references Python 3.
Python Mac Gui
Pipenv & Virtual Environments¶
The next step is to install Pipenv, so you can install dependencies and manage virtual environments.
A Virtual Environment is a tool to keep the dependencies required by different projectsin separate places, by creating virtual Python environments for them. It solves the“Project X depends on version 1.x but, Project Y needs 4.x” dilemma, and keepsyour global site-packages directory clean and manageable.
For example, you can work on a project which requires Django 1.10 while alsomaintaining a project which requires Django 1.8.
So, onward! To the Pipenv & Virtual Environments docs!
Python Apps Examples
This page is a remixed version of another guide,which is available under the same license.